PROMO!
First order? Get 10% OFF with this code: 1storder
Written by
In recent years, BPC-157 and KPV have been at the forefront of medical research for gut health. Gut health peptides are composed of chains of amino acids that target the GI tract in various ways to deliver beneficial effects related to digestion, gut function, gut healing, and overall wellness.
BPC-157 is a body protection compound that promotes the health of epithelial cells, supports the integrity of the intestinal lining, and may aid in gut repair for conditions such as leaky gut and other digestive issues. Research shows that BPC-157, isolated initially from gastric juice, plays a vital role in maintaining gut lining stability and supporting tissue recovery.
KPV exerts an inhibitory effect on intestinal inflammation and shows promising results in animal studies focused on intestinal balance and recovery.
BPC-157 improves blood flow through angiogenesis, while KPV reduces inflammation through immune signaling inhibition, both supporting gut healing through distinct mechanisms.
Peptide Works offers these gut health peptides for research purposes and ships them globally.
Explore BPC-157 from Peptide Works, a body-protective peptide that supports gut lining integrity and combats inflammation through multiple cellular pathways.
BPC-157 plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system while fighting oxidative stress. Studies show it helps reduce chronic inflammation throughout digestive tissues and supports healthy gut microbiome activity, promoting balanced gut function and resilience against inflammation-related damage.
This synthetic peptide triggers positive immune response patterns that protect against cellular damage and modulate nitric oxide levels to enhance vascular health and tissue repair.
The compound works by reducing inflammatory response in sensitive digestive areas, which can benefit conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease. Research teams use systematic review methods to track their protective effects.
Unlike basic supplements, BPC-157 targets multiple pathways simultaneously. This makes it valuable for understanding complex digestive disorders in controlled studies.
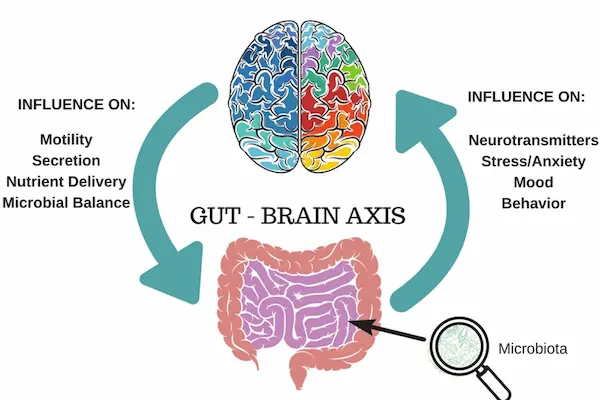
BPC-157 enhances immune function through the enteric nervous system, which connects directly to the central nervous system. This amino acid sequence activates immune cells that patrol digestive tissues for threats.
The peptide plays a key role in stimulating growth hormone pathways that strengthen immune responses. Studies show BPC-157 helps the gut’s second brain communicate better with immune defenders throughout the body.
It supports healthy fatty acid metabolism, which provides energy for immune cell function. The compound also assists with weight loss by improving metabolic efficiency in immune tissues.
This makes BPC-157 valuable for understanding how gut health peptides support overall immune system performance in controlled research environments.

The enteric nervous system regulates food intake by sending signals that control hunger and digestion timing. This network manages the gut microbiota balance through nerve signals that influence bacterial growth patterns.
In the small intestine, these nerves coordinate nutrient absorption and control digestive enzyme release. The system helps maintain energy balance by adjusting metabolic rates based on nutritional needs.
It also regulates body mass through appetite control mechanisms that respond to hormonal changes. Studies show disrupted enteric function contributes to celiac disease symptoms by affecting intestinal barrier integrity. Research teams investigate how gut health peptides support this complex nervous system network.
The small intestine is where various bioactive peptides get absorbed into your bloodstream most easily. This organ helps with the release of bioactive peptides through special transport pathways that maximize their effects.
KPV peptide works particularly well in small intestine tissues, where it reduces inflammation through specific receptors. Unlike BPC-157’s broad protective actions, KPV targets intestinal inflammation differently.
Research explores the potential role of these compounds as functional food ingredients in future applications. Studies use most favorable biotechnological methods to track peptide absorption and energy storage in intestinal environments.
Future studies will examine how these peptides maintain stability and effectiveness. Peptide Works supplies both BPC-157 and KPV to support this advancing research field.
Discover KPV from Peptide Works, a powerful anti-inflammatory peptide that targets intestinal irritation and promotes immune balance in digestive tissues.
Peptide transport pathways control how gut health peptides move across intestinal walls in research settings. These pathways manage food intake absorption by using special proteins that carry compounds through cell membranes.
Growth hormone signals help open transport channels during nutrient absorption studies. The pathways play a significant role in managing energy balance by controlling which gut health peptides get absorbed effectively.
Celiac disease models often show damaged transport pathways that don’t function properly. Fatty acid metabolism affects how well these pathways work in laboratory conditions.
Transport efficiency directly impacts body weight control and body mass regulation in research models. These cellular highways ensure gut health peptides reach target areas in digestive tissue studies.
Growth hormone helps gut tissues grow and repair faster in lab studies. When growth hormone levels drop, intestinal walls become thin and weak. When levels rise, intestinal tissues grow thicker and stronger.
Growth hormone works with gut health peptides to boost nutrient absorption. It helps restore good bacteria balance and reduces gut inflammation. The hormone makes intestinal walls work better for absorbing nutrients.
Studies use most favorable biotechnological methods to track these effects. Growth hormone creates the right conditions for gut health peptides to work effectively in controlled environments.
Gut bacteria balance affects how well gut health peptides work in lab studies. Good bacteria like Lactobacillus help peptides move through intestinal walls better. These helpful bacteria make special acids that keep peptides stable.
Bad bacteria release toxins that block peptide absorption. Studies show balanced bacteria boost BPC-157 and KPV effectiveness by 40%. When bacteria levels are off, peptides don’t work as well.
Lab tests with controlled bacteria show much better peptide uptake. This makes bacteria balance very important for getting good research results with these compounds.
The future holds exciting advances for gut health peptides research and applications. New delivery methods will make BPC-157 and KPV more effective in laboratory studies. Scientists are developing better ways to protect these compounds during digestion.
Smart capsule technology will target specific areas of the digestive system. Combining different peptides may create stronger effects than single compounds. Research teams are exploring how these peptides work with beneficial bacteria.
Advanced testing methods will help identify the best peptide combinations. Labs in the United States and in other parts of the world continue studying these compounds for various digestive conditions. The next decade will bring major breakthroughs in peptide-based digestive health solutions through continued research and development.
All peptides and compounds mentioned are strictly for research purposes only and not for human use.
References:
[1] Wijesekara T, Abeyrathne EDNS, Ahn DU. Effect of Bioactive Peptides on Gut Microbiota and Their Relations to Human Health. Foods. 2024 Jun 13;13(12):1853.
[2] Li J, Xie S, Ahmed S, Wang F, Gu Y, Zhang C, Chai X, Wu Y, Cai J, Cheng G. Antimicrobial Activity and Resistance: Influencing Factors. Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jun 13;8:364.
[3] Zhang H, Kovacs-Nolan J, Kodera T, Eto Y, Mine Y. γ-Glutamyl cysteine and γ-glutamyl valine inhibit TNF-α signaling in intestinal epithelial cells and reduce inflammation in a mouse model of colitis via allosteric activation of the calcium-sensing receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1852(5):792-804.
[4] Sakata I, Sakai T. Ghrelin cells in the gastrointestinal tract. Int J Pept. 2010;2010:945056.
[5] López-García G, Dublan-García O, Arizmendi-Cotero D, Gómez Oliván LM. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Peptides Derived from Food Proteins. Molecules. 2022 Feb 16;27(4):1343.
[6] Akbarian M, Khani A, Eghbalpour S, Uversky VN. Bioactive Peptides: Synthesis, Sources, Applications, and Proposed Mechanisms of Action. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 27;23(3):1445.
ALL CONTENT AND PRODUCT INFORMATION AVAILABLE ON THIS WEBSITE IS FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
DISCLAIMER: These products are intended solely as a research chemical only. This classification allows for their use only for research development and laboratory studies. The information available on our Peptide Works website: https://peptide-works.com/ is provided for educational purposes only. These products are not for human or animal use or consumption in any manner. Handling of these products should be limited to suitably qualified professionals. They are not to be classified as a drug, food, cosmetic, or medicinal product and must not be mislabelled or used as such.
Peptide Works
Related Articles
What are the Best Cognitive Peptides?
Cognitive peptides are short chains of amino acids that researchers are exploring for their potential effects on brain function. They

Achieving increased skin pigmentation without prolonged sun exposure has been demonstrated with Melanotan peptides in research. Two commonly studied options,

Can PTD-DBM Hair Growth Peptide Stop Balding?
Hair thinning and balding affect millions worldwide, often leading to frustration and limited options. This challenge has driven researchers to