PROMO!
First order? Get 10% OFF with this code: 1storder
Written by

Gonadorelin Peptide and HCG are two compounds that work differently in scientific studies. Both boost hormone levels but use different pathways.
Gonadorelin is a small peptide with 10 amino acids. HCG is much bigger with 237 amino acids. Studies show both give good results. They work through different body systems.
Gonadorelin targets brain signals. HCG acts like natural hormones. At Peptide Works, we supply both compounds globally for scientific purposes only.
Researchers choose the right compound based on their specific study needs. This brings us to how each peptide actually works.
Explore Gonadorelin Peptide from Peptide Works, a fast-acting peptide studied for its role in hormone signaling and LH stimulation.
Gonadorelin Peptide works by mimicking natural GnRH signals from the brain. It binds to pituitary receptors and triggers luteinizing hormone release within minutes.
This creates a natural cascade effect through the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. HCG peptide works differently by acting directly like luteinizing hormone itself. It bypasses brain signals and goes straight to target cells.
HCG has a longer half-life, so effects last hours instead of minutes. Both pathways stimulate hormone production but through completely different mechanisms. For broader insights into compounds studied for reproductive and hormonal signaling, explore our blog on Fertility Peptides .
Researchers choose based on whether their study protocol needs quick responses or sustained effects. To understand this better, we need to look at the body’s hormone system.
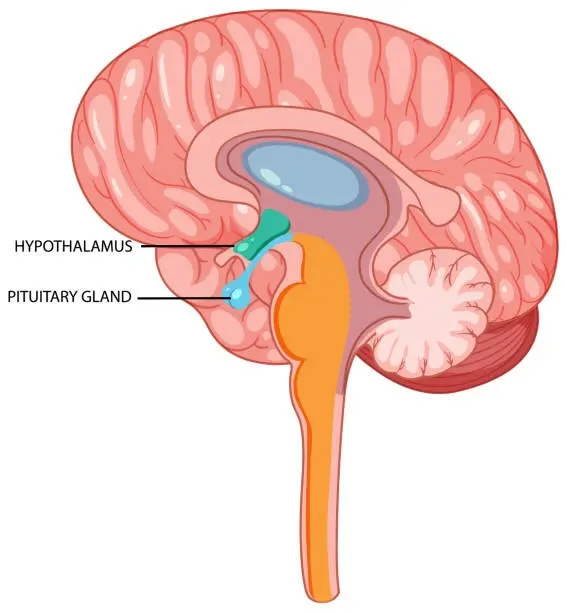
The hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis is the body’s main hormone control system. It starts in the brain’s hypothalamus, which makes GnRH naturally.
This signal travels to the pituitary gland below the brain. The pituitary then releases luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone. These hormones travel through blood to reach target organs.
Gonadorelin Peptide works by copying this natural GnRH signal exactly. This makes it perfect for studying normal hormone pathways. Scientists use this system to understand how hormones work in living organisms.
The axis controls many important body functions. But why does HCG last so much longer? It comes down to structure.
HCG peptide has a much longer half-life because of its complex protein structure. It contains two connected protein chains called alpha and beta subunits.
These chains protect HCG from breaking down quickly in blood. Gonadorelin Peptide has only 10 amino acids in a simple chain. This small size makes it break down faster through natural enzymes.
HCG’s half-life is 24-34 hours while Gonadorelin lasts only 2-10 minutes. The size difference explains why researchers pick HCG for longer studies.
This duration difference affects how scientists design their experiments. The way HCG is built makes all the difference in how well it works.

HCG peptide has a much more complex structure that makes it more effective. It weighs 36,700 g/mol compared to Gonadorelin Peptide’s tiny 1,182 g/mol.
HCG contains 30% carbohydrate chains attached to its protein structure. These sugar molecules protect HCG from breaking down quickly in research conditions. HCG also has two connected protein chains called alpha and beta subunits.
The beta subunit has an extra 31-amino acid tail that increases stability. This complex structure gives HCG an 80-fold longer effectiveness period than similar compounds. Carbohydrate chains critically impact peptide effectiveness.
Discover HCG Peptide from Peptide Works, a long-lasting compound explored for its LH-mimicking effects and hormone regulation support.
Carbohydrate chains make HCG much more effective than Gonadorelin Peptide through several protection mechanisms. These sugar molecules increase membrane permeability by 3-4 times compared to non-glycosylated peptides.
They also protect HCG from enzyme breakdown that destroys simpler peptides. Carbohydrate chains enhance bioavailability and reduce clearance rates significantly.
HCG contains 30% carbohydrates while Gonadorelin has zero sugar protection. The glycosylation also improves receptor binding strength and signal transduction effectiveness.
This carbohydrate shield explains why HCG outperforms smaller peptides in research applications requiring sustained activity. On the flip side, Gonadorelin doesn’t have this protection.
Gonadorelin Peptide breaks down much faster than HCG because it has no protective mechanisms. It degrades through three different pathways including deamidation, hydrolysis, and amino acid changes.
The peptide only stays stable for 70 days at room temperature compared to HCG’s years-long stability. Gonadorelin requires special storage at pH 5.0 with acetate buffers to prevent breakdown.
Without carbohydrate protection like HCG has, Gonadorelin gets destroyed by enzymes within 10-40 minutes. This rapid breakdown makes it less effective for research applications needing sustained activity over time. So what does all this mean for researchers?
Both Gonadorelin Peptide and HCG offer unique advantages for different research applications. HCG proves more effective for long-term studies requiring sustained hormone activity.
Its complex structure and carbohydrate protection provide 80-fold longer effectiveness than Gonadorelin Peptide. However, Gonadorelin excels in studies needing precise timing and rapid hormone responses.
The choice depends on specific research goals and duration requirements. Future research will likely utilize both compounds for their distinct strengths. HCG dominates extended studies while Gonadorelin serves short-term applications better.
Peptide Works provides both research compounds with proper documentation and worldwide shipping to support advancing scientific discoveries.
All products discussed are supplied for research purposes only and are not intended for human use.
[1] Cole LA. New discoveries on the biology and detection of human chorionic gonadotropin. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2009 Jan 26;7:8.
[2] Stenman UH, Tiitinen A, Alfthan H, Valmu L. The classification, functions and clinical use of different isoforms of HCG. Hum Reprod Update. 2006 Nov-Dec;12(6):769-84.
[3] Martínez M, Mapletoft RJ, Kastelic JP, Carruthers T. The effects of 3 gonadorelin products on luteinizing hormone release, ovulation, and follicular wave emergence in cattle. Can Vet J. 2003 Feb;44(2):125-31.
[4] Nwabuobi C, Arlier S, Schatz F, Guzeloglu-Kayisli O, Lockwood CJ, Kayisli UA. hCG: Biological Functions and Clinical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 22;18(10):2037.
ALL CONTENT AND PRODUCT INFORMATION AVAILABLE ON THIS WEBSITE IS FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
DISCLAIMER: These products are intended solely as a research chemical only. This classification allows for their use only for research development and laboratory studies. The information available on our Peptide Works website: https://peptide-works.com/ is provided for educational purposes only. These products are not for human or animal use or consumption in any manner. Handling of these products should be limited to suitably qualified professionals. They are not to be classified as a drug, food, cosmetic, or medicinal product and must not be mislabelled or used as such.
Peptide Works
Related Articles
What are the Best Cognitive Peptides?
Cognitive peptides are short chains of amino acids that researchers are exploring for their potential effects on brain function. They

Achieving increased skin pigmentation without prolonged sun exposure has been demonstrated with Melanotan peptides in research. Two commonly studied options,

Can PTD-DBM Hair Growth Peptide Stop Balding?
Hair thinning and balding affect millions worldwide, often leading to frustration and limited options. This challenge has driven researchers to