
PROMO!
First order? Get 10% OFF with this code: 1storder
Written by

Longevity peptides are short chains of amino acids that studies show may help support healthy aging and cell health at the cellular level. Research points to peptides Epithalon and MOTS-c, along with the coenzyme NAD+, as examples that may help support DNA repair, cellular energy, and metabolism.
At Peptide Works, we offer these peptides for research only, helping researchers study their effects safely. These peptides are not for human use but are important in understanding how biological aging might be slowed down.
Understanding their general benefits leads us to examine how these peptides specifically support key cellular functions, a foundation for exploring related biological processes involved in longevity.
Explore Epithalon from Peptide Works, a peptide studied for its role in activating telomerase to support DNA integrity and cell longevity.
Longevity peptides work in natural ways to support DNA repair and keep cells healthy in research studies. For example, Epithalon activates an enzyme called telomerase, one of the key mechanisms of action studied in longevity research.
This enzyme makes telomeres longer, which protects DNA when cells divide and slows down cell aging. NAD+ helps cells make energy and is very important for fixing damaged DNA. This makes cells stronger against stress and aging by helping maintain healthy energy levels and lowering oxidative stress. MOTS-c helps maintain mitochondrial health and supports metabolism by improving mitochondrial function and reducing mitochondrial dysfunction.
This protects cells from damage and maintains balanced cellular function. To better understand these effects, it’s important to focus on Epithalon’s role in cellular protection.
Discover NAD+ peptide from Peptide Works, a vital coenzyme researched for boosting cellular energy and aiding DNA repair processes.
Epithalon is a synthetic peptide and one of the specific peptides known to activate telomerase, an enzyme found in the body. Telomerase works by making telomeres longer. Telomeres protect cells by covering the ends of chromosomes during cell division. Epithalon binds to certain DNA areas in the telomerase gene, which turns on telomerase production.
When telomeres are longer, DNA is less likely to be damaged. This slows down cell aging. By activating telomerase, Epithalon helps cells remain healthier for longer.
Research shows that this process may support cellular longevity. Peptide Works offers Epithalon for research use only, following strict quality control standards to help researchers study its effects safely.
This understanding of telomerase naturally highlights the importance of telomeres and their vital role.
Shop MOTS-c at Peptide Works, a mitochondrial peptide investigated for supporting metabolism, stress response, and cellular resilience.
Telomeres are short DNA sequences found at the ends of chromosomes. They protect genetic material from damage during cell division and help regulate cell proliferation.
Every time a cell divides, telomeres become shorter, which limits how many times a cell can safely divide. When telomeres get too short, cells stop dividing and enter a state called cellular senescence, where they stay alive but no longer grow.
This process is linked to signs of aging, slower tissue repair, lower bone density, and age-related diseases. Keeping telomeres long helps cells stay healthy, so telomeres are a biological clock for the aging process. Understanding cellular senescence is a key step in examining aging.
Cellular senescence happens when a cell permanently stops dividing due to damage or old age. These senescent cells don’t die; they build up in tissues as we get older.
Over time, senescent cells can send out signals that cause inflammation and slow tissue repair. This buildup is linked to signs of aging, like weaker healing and more age-related diseases.
The immune function plays an important role in clearing these senescent cells, but it becomes less effective with age, allowing the cells to accumulate. Removing them in research can help tissues work better, showing their impact on how our bodies age and stay healthy.
Senescent cells influence aging further by causing inflammation, which requires careful examination.
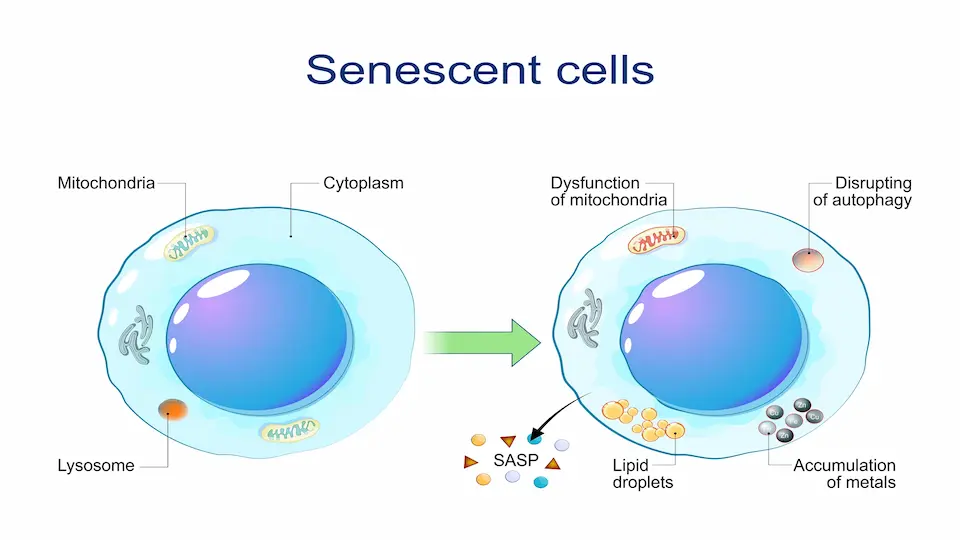
Senescent cells release signals called SASP that cause chronic inflammation in tissues. This process, known as inflammaging, worsens as these cells build up with age.
Chronic inflammation can harm healthy cells, slow tissue repair, and raise the risk of age-related diseases. It can also affect cognitive function, contributing to cognitive decline over time. Longevity peptides like Epithalon and NAD+ have been studied for their potential to influence cellular aging and reduce inflammation in research.
MOTS-c supports cell energy balance, which may help lower damaging inflammation in cells and promote antioxidant activity that protects against oxidative damage. These peptides provide key insights into aging in scientific studies.
Building on this, it is important to see how longevity peptides assist in cell repair beyond energy metabolism.
Longevity peptides help fix cells by supporting DNA repair, tissue growth, and healthy cell survival in studies. Epithalon has been shown to activate telomerase, helping protect chromosomes and improve DNA stability.
NAD+ acts as a helper for enzymes that repair DNA and keep cells strong after damage. MOTS-c helps cells recover from stress by protecting mitochondria and adjusting gene activity for cell health.
These actions suggest that longevity peptides may help promote healing, slow aging, and support tissue and immune system health, according to current research. Some studies in animal models also help scientists learn more about how these peptides work in the lab. Ongoing research continues to find new ways these peptides may support healthy aging.
Research on longevity peptides is moving forward with new discoveries every year. Scientists are learning more about how peptides support healthy aging and cell repair in studies.
Many experts hope these advances will offer more ways to study age-related changes and recovery. As online retailers, Peptide Works brings you trusted research peptides for scientific use, with fast worldwide shipping.
Our focus is helping researchers explore these new frontiers in longevity and share the latest updates in aging science.
All products discussed are supplied for research purposes only and are not intended for human use.
[1] Anisimov VN, Khavinson VKh, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA, et al. Effect of Epitalon on biomarkers of aging, life span and spontaneous tumor incidence in female Swiss-derived SHR mice. Biogerontology. 2003;4(4):193-202.
[2] Araj SK, Brzezik J, Mądra-Gackowska K, Szeleszczuk Ł. Overview of Epitalon-Highly Bioactive Pineal Tetrapeptide with Promising Properties. Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 17;26(6):2691.
[3] Yue X, Liu SL, Guo JN, Meng TG, et al. Epitalon protects against post-ovulatory aging-related damage of mouse oocytes in vitro. Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Apr 12;14(7):3191-3202.
[4] Yaku K, Okabe K, Nakagawa T. NAD metabolism: Implications in aging and longevity. Ageing Res Rev. 2018 Nov;47:1-17.
[5] Fuku N, Pareja-Galeano H, Zempo H, Alis R, et al. The mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c: a player in exceptional longevity? Aging Cell. 2015 Dec;14(6):921-3.
ALL CONTENT AND PRODUCT INFORMATION AVAILABLE ON THIS WEBSITE IS FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
DISCLAIMER: These products are intended solely as a research chemical only. This classification allows for their use only for research development and laboratory studies. The information available on our Peptide Works website: https://peptide-works.com/ is provided for educational purposes only. These products are not for human or animal use or consumption in any manner. Handling of these products should be limited to suitably qualified professionals. They are not to be classified as a drug, food, cosmetic, or medicinal product and must not be mislabelled or used as such.
Peptide Works
Related Articles
Cartalax Benefits for Aging: Supporting Joint and Tissue Health Naturally
Aging affects how joints move and how tissues handle daily stress. Over time, movement may feel less smooth, and tissues
Why Is the Cartalax Peptide a Game-Changer for Cartilage Health?
The cartalax peptide stands out in cartilage health research due to its defined tripeptide structure and its use as a
Bronchogen: A Potential Breakthrough for COPD Patients
Bronchogen is a short peptide with the sequence Ala-Glu-Asp-Leu (AEDL) studied for its effects on lung tissue structure and airway