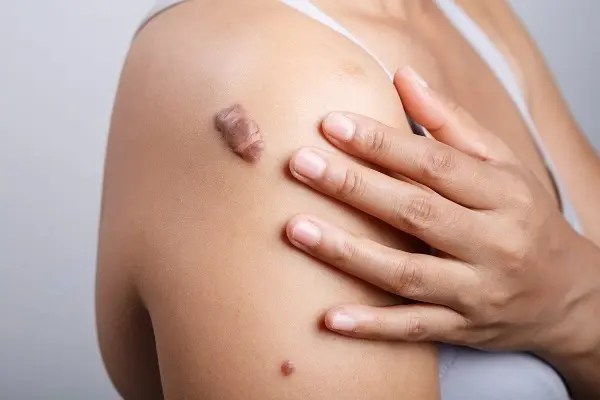
Keloids form when scar tissue grows excessively, leading to raised, firm scars that can be hard to treat. Many keloid treatment therapy options, such as surgery and steroid injections, often provide limited success.
FOXO4-DRI is a peptide studied for its effect on cellular senescence, a process involved in scar formation. Research suggests targeting FOXO4 pathways may help reduce abnormal scar growth.
Peptide Works is an online retailer supplying peptides like FOXO4-DRI, GHK-Cu, BPC-157, and others strictly for research use related to keloid treatment therapy and scar management. All products are not for human use.
Understanding the role of cellular processes behind keloid formation provides insight into why new treatments are being researched.
Explore FOXO4-DRI from Peptide Works, a peptide that targets cellular senescence to help reduce abnormal scar tissue growth in keloid treatment therapy.
How Does Cellular Senescence Affect Keloid Treatment Therapy?
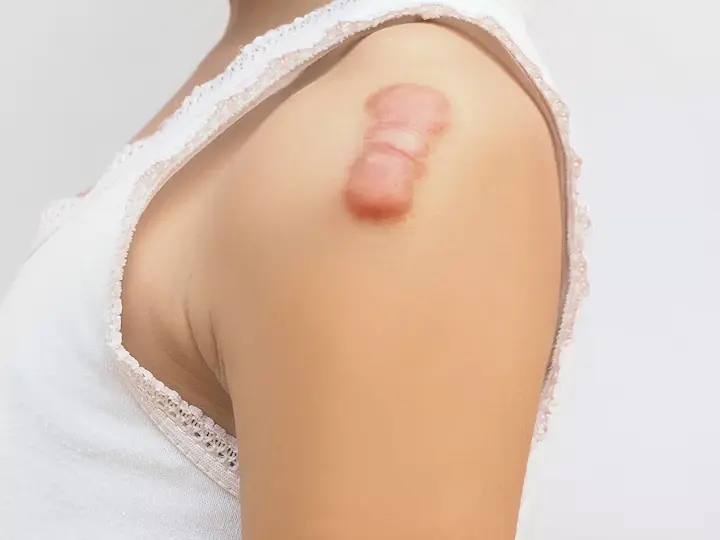
Cellular senescence happens when damaged cells stop growing but do not die. In keloids, these cells build up and cause scar tissue to thicken.
This makes scars firm and hard to heal. Research shows that removing senescent cells may help reduce keloid scars. Peptides like FOXO4-DRI are studied for their ability to clear these cells safely.
Other peptides such as GHK-Cu and BPC-157 support skin repair by promoting new tissue growth and reducing inflammation.
These advances give hope for improved keloid treatment therapy in the future. Skin repair mechanisms are essential in controlling scar development.
Discover GHK-Cu at Peptide Works, a copper-binding peptide known to promote skin repair, reduce inflammation, and support healthy collagen synthesis.
Why Is Skin Repair Crucial in Keloid Treatment Therapy?
Healthy skin repair is key to stopping keloids. When a wound heals poorly, scar tissue builds up and becomes raised. Good skin repair helps wounds close faster and makes scars less likely to form thick tissue.
Research shows that peptides like GHK-Cu boost skin healing by helping new cells grow and making the skin stronger.
BPC-157 also supports tissue repair by reducing inflammation and building healthy skin layers.
Better skin repair means fewer keloid scars and better results from keloid treatment therapy. Inflammation has a direct impact on how scars develop and heal.
Checkout BPC-157 from Peptide Works, a peptide that accelerates tissue repair and reduces inflammation to enhance wound healing and scar management.
How Does Inflammation Impact Scar Formation and Healing?
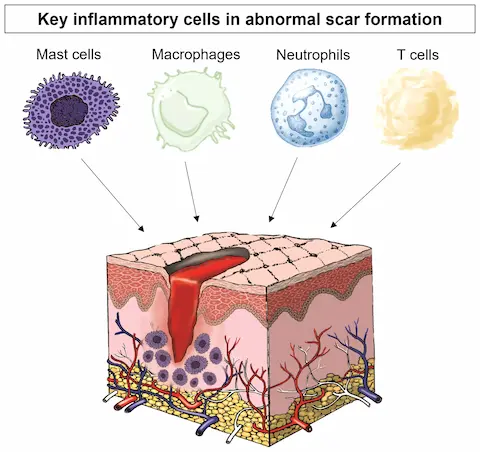
Inflammation happens early after a skin injury and helps clean the wound. Too much inflammation makes scars bigger and thicker.
Studies show that when inflammation is controlled, scar tissue stays softer and heals better. Peptides such as BPC-157 and GHK-Cu lower excess inflammation in wounds and help normal tissue grow.
These peptides also boost blood flow and collagen, which are important for quicker recovery and less severe scars. Managing inflammation smartly may improve scar appearance and speed up healing.
Collagen is a major element influencing scar structure and strength.
What Role Does Collagen Play in Scar Healing and Keloid Formation?
Collagen is the main protein building block in skin and scars. After injury, it helps new tissue form and gives repaired skin strength.
In keloids, too much collagen mainly types I and III is made and arranged in thick, dense bundles. These bundles stack randomly, making scars bigger and firmer than normal.
New research shows that the right balance of collagen types is important for softer, less-visible scars. Peptides like GHK-Cu and BPC-157 have been studied for helping manage healthy collagen levels and scar appearance by supporting normal tissue repair, not just stopping excess.
At Peptide Works, we offer a variety of research peptides, including some of the best tissue repair peptides for exploring cellular growth and regeneration pathways in laboratory studies. The overall process of tissue repair can determine whether a scar develops into a keloid.
How Does Tissue Repair Influence Keloid Scar Formation?

Tissue repair starts when skin gets damaged. If healing breaks down, too many repair cells build new tissue, causing keloids.
Research shows fibroblasts in keloid scars make extra collagen, changing scar size and thickness. Good tissue repair may lower this risk and keep scars from spreading.
Researchers study peptides for their effects on tissue repair, scar softness, and growth. GHK-Cu and BPC-157 help normal healing and control cell growth linked to keloid treatment therapy. Fibroblasts play a central role in scar development and peptide research.
What Role Do Fibroblasts Play in Keloid Scar Formation?
Fibroblasts are main cells in skin repair. In keloid scars, these cells make too much collagen, which causes thick, raised scars.
Unlike normal fibroblasts, keloid fibroblasts multiply faster and respond more to growth signals. Their extra activity leads to more scar tissue forming over time.
Researchers study how peptides such as GHK-Cu and BPC-157 may help manage fibroblast behavior and reduce scar buildup in keloid treatment therapy.
Understanding fibroblast roles can improve scar research. Considering all advances, peptides hold potential for future therapies.
What Is the Future of Peptides in Keloid Treatment Therapy?
Peptides show promise for the future of keloid treatment therapy. Current research is testing how compounds like FOXO4-DRI, GHK-Cu, and BPC-157 affect scar growth and tissue repair.
Early studies suggest that some peptides may help control abnormal collagen production and reduce scar tissue in the lab. As science progresses, new peptides could make it easier to manage tough, raised scars where older treatments fall short.
More research is still needed before peptide therapies become standard for keloid treatment therapy. For now, all peptide research is for lab use only, but ongoing studies may lead to new options for keloid care in the future.
All products discussed are supplied for research purposes only and are not intended for human use.
References
[1] Huang Y, He Y, Makarcyzk MJ, Lin H. Senolytic Peptide FOXO4-DRI Selectively Removes Senescent Cells From in vitro Expanded Human Chondrocytes. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Apr 29;9:677576.
[2] Zhu M, Goetsch SC, Wang Z, et al. FoxO4 promotes early inflammatory response upon myocardial infarction via endothelial Arg1. Circ Res. 2015 Nov 6;117(11):967-77.
[3] Liu W, Li Y, Luo B. Current perspective on the regulation of FOXO4 and its role in disease progression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Feb;77(4):651-663.
[4] Seiwerth S, Milavic M, Vukojevic J, Gojkovic S, et al. Stable Gastric Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and Wound Healing. Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 29;12:627533.
[5] Pickart L, Vasquez-Soltero JM, Margolina A. GHK Peptide as a Natural Modulator of Multiple Cellular Pathways in Skin Regeneration. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:648108.