PROMO!
First order? Get 10% OFF with this code: 1storder
Written by

Are you looking for research compounds that show promise in muscle growth studies? Muscle building peptides are exciting research tools that scientists study in labs. These research peptides work by boosting growth hormone release and improving protein synthesis in controlled lab settings.
Compounds like Ipamorelin, CJC-1295, MGF, and MK677 show strong potential in research studies. Research shows that muscle building peptides can significantly increase lean muscle mass in laboratory models. This makes them valuable tools for understanding how muscles grow.
At Peptide Works, we supply high-quality research peptides to scientists and researchers worldwide. We support studies that explore how these compounds affect muscle growth pathways.
To appreciate the potential of these peptides, it is essential to understand how they trigger the release of growth hormone, the hormone that sets the stage for muscle growth.
Discover MGF from Peptide Works, a research peptide that enhances local growth factor activity to support targeted muscle tissue recovery.
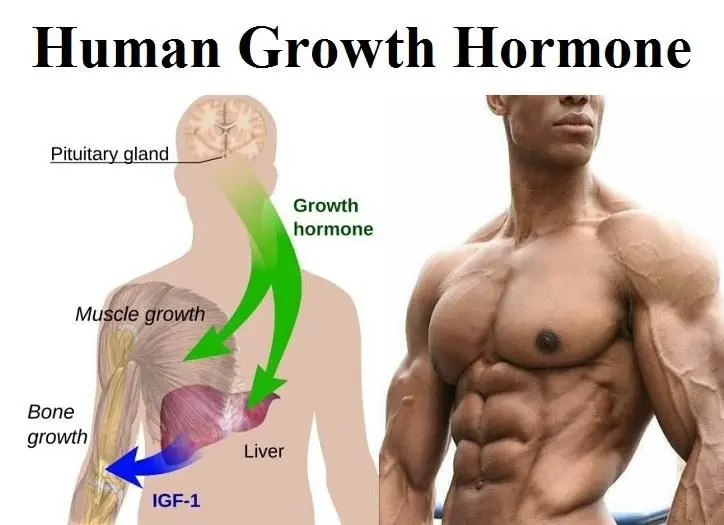
Muscle building peptides work by encouraging your pituitary gland to release more natural growth hormone. For example, Ipamorelin targets ghrelin receptors to create a pulsatile release pattern, while CJC-1295 prolongs growth hormone elevation over several hours. MK-677 functions as a ghrelin mimetic, gradually increasing hormone levels over time. MGF operates differently, subtly enhancing local growth factor activity in muscle tissue.
These peptides initiate signaling by binding to specific receptors in the brain, triggering a cascade that results in increased growth hormone. Higher growth hormone levels then signal the liver to produce IGF-1, linking hormonal stimulation to muscle-building pathways.
Once growth hormone is elevated, IGF-1 carries the signal directly to the muscles, making it crucial to understand its role in actual tissue growth and recovery.
Explore CJC-1295 from Peptide Works, a research compound that maintains elevated growth hormone levels to support faster muscle recovery and stronger regeneration.
IGF-1 is a vital regulator of protein production and turns on satellite cells, which help repair damaged muscle fibers. It drives muscle growth by enlarging fibers and improving tissue recovery. Research shows that higher IGF-1 levels are linked to faster recovery and better adaptation to training.
Muscle building peptides contribute indirectly: while Ipamorelin and CJC-1295 elevate GH, IGF-1 mediates local anabolic effects in muscles, creating an environment conducive to regeneration rather than just hormone circulation.
With the hormonal foundation in place, muscle protein synthesis determines whether repaired fibers become stronger and thicker.
Check out Ipamorelin from Peptide Works, a muscle building peptide that stimulates natural growth hormone release to support lean muscle development.
Protein synthesis rebuilds muscle tissue using amino acids after exercise-induced damage. This process determines how muscles repair, strengthen, and grow larger.
Leucine plays a key role by activating mTORC1 at the ribosome level, effectively telling the cell to begin assembling new proteins. Research models show that when leucine availability is optimal, the ribosomal machinery works more efficiently, increasing the rate of muscle repair and hypertrophy.
Peptides like CJC-1295 indirectly enhance this environment by sustaining IGF-1 and GH signaling, which primes mTOR activation. This makes ribosomes more responsive to amino acid availability, promoting faster and more efficient muscle growth.
To fully understand how protein synthesis is fueled, it’s essential to look at which amino acids provide the building blocks that make this growth possible.
Explore MK-677 from Peptide Works, a ghrelin mimetic that gradually boosts growth hormone levels to aid in muscle growth studies.
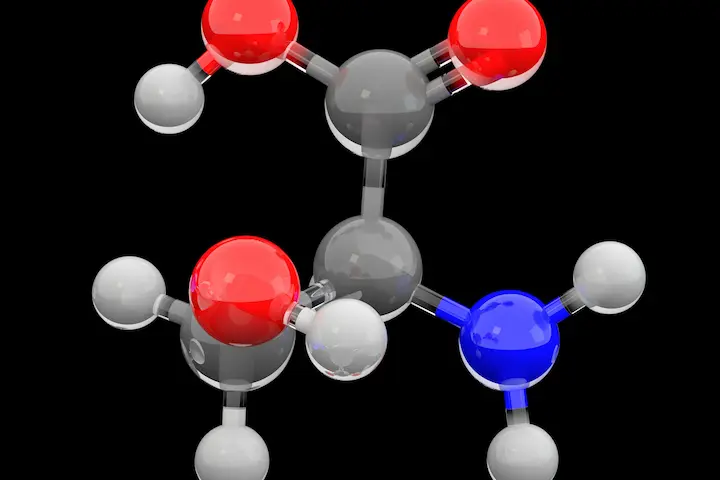
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), leucine, isoleucine, and valine are the most important for muscle building. While leucine triggers protein synthesis at the ribosome, isoleucine and valine support energy metabolism and help maintain a positive nitrogen balance, ensuring net protein gain.
These amino acids are essential for sustaining prolonged training and recovery cycles. By combining GH/IGF-1–enhancing peptides with adequate BCAAs, researchers create conditions where both synthesis and preservation of muscle mass are optimized.
With amino acids supplying the building blocks, it’s critical to understand how mTOR integrates all these signals to control growth at the molecular level.
mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) is the cell’s central “growth switch.” When activated by IGF-1 or leucine, it initiates ribosome-driven protein assembly, translating growth signals into tangible muscle fibers.
Research-grade peptides amplify upstream signals, but mTOR is where these signals converge, controlling the speed and scale of muscle fiber expansion.
While mTOR controls growth chemically, actual muscle adaptation also requires physical load, which is why mechanical tension is essential to examine.

Mechanical tension is the muscle’s “go” cue. When fibres face heavy load or prolonged stretch, mechanoreceptors tell the cell to speed up repair and protein building, flipping on mTOR and other anabolic switches that create thicker, stronger fibres.
That same tension also wakes up satellite cells, giving muscle new nuclei for even more protein storage. Muscle building peptides that stimulate growth hormone and IGF-1, such as those available for research at Peptide Works, amplify the mTOR response sparked by tension.
Understanding how load and muscle building peptides interact lets scientists fine-tune training variables and experimental protocols to maximise lean-mass gains.
Finally, considering both chemical and mechanical pathways highlights the broader potential of these peptides for research and future therapies.
Muscle growth now follows a simple map: tension starts the signal, mTOR flips the switch, amino acids build new tissue, and growth-hormone pathways keep progress steady.
Muscle building peptides like Ipamorelin, CJC-1295, MGF, and MK-677 sold online by Peptide Works allow scientists to fine-tune each step of this process.
Early data indicate these muscle building peptides may support faster recovery, stronger fibers, and potential future therapies for sport, rehabilitation, and age-related muscle loss.
All products discussed are supplied for research purposes only and are not intended for human use.
[1] Sinha DK, Balasubramanian A, Tatem AJ, Rivera-Mirabal J, et al. Beyond the androgen receptor: the role of growth hormone secretagogues in the modern management of body composition in hypogonadal males. Transl Androl Urol. 2020 Mar;9(Suppl 2):S149-S159.
[2] Teichman SL, Neale A, Lawrence B, Gagnon C, et al. Prolonged stimulation of growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor I secretion by CJC-1295, a long-acting analog of GH-releasing hormone, in healthy adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Mar;91(3):799-805.
[3] Nass R, Pezzoli SS, Oliveri MC, Patrie JT, et al. Effects of an oral ghrelin mimetic on body composition and clinical outcomes in healthy older adults: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2008 Nov 4;149(9):601-11.
[4] Iida K, Itoh E, Kim DS, del Rincon JP, et al. Muscle mechano growth factor is preferentially induced by growth hormone in growth hormone-deficient lit/lit mice. J Physiol. 2004 Oct 15;560(Pt 2):341-9.
[5] Kandalla PK, Goldspink G, Butler-Browne G, Mouly V. Mechano Growth Factor E peptide (MGF-E), derived from an isoform of IGF-1, activates human muscle progenitor cells and induces an increase in their fusion potential at different ages. Mech Ageing Dev. 2011 Apr;132(4):154-62.
ALL CONTENT AND PRODUCT INFORMATION AVAILABLE ON THIS WEBSITE IS FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
DISCLAIMER: These products are intended solely as a research chemical only. This classification allows for their use only for research development and laboratory studies. The information available on our Peptide Works website: https://peptide-works.com/ is provided for educational purposes only. These products are not for human or animal use or consumption in any manner. Handling of these products should be limited to suitably qualified professionals. They are not to be classified as a drug, food, cosmetic, or medicinal product and must not be mislabelled or used as such.
Peptide Works
Related Articles
What are the Best Cognitive Peptides?
Cognitive peptides are short chains of amino acids that researchers are exploring for their potential effects on brain function. They

Achieving increased skin pigmentation without prolonged sun exposure has been demonstrated with Melanotan peptides in research. Two commonly studied options,

Can PTD-DBM Hair Growth Peptide Stop Balding?
Hair thinning and balding affect millions worldwide, often leading to frustration and limited options. This challenge has driven researchers to